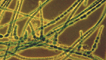
1. Criteria for solid cultures
1.1. Growth type
1.1.1. Spreading growth : Growth that indicates movements of trichomes or hormogonia away from the streaks.
Type:
Generalized: Growth covers entire plate.
Localized: Spreading in the vicinity of the streaks.
Aggregation :
Diffuse: Absence of discernable structures in the mat. Growth spreads out as a delicate cottony patch on and/or under agar surface; e.g., some homocystous filamentous strains with thin trichomes.
Fibrous: Felt-like mat; e.g., Calothrix and some homocystous filamentous strains with thick trichomes.
Ropey: Having clearly discernable wavy structures resulting from the formation of bundles; e.g., many Anabaena .
Coiled: Having circular bundles; e.g., some Anabaena . 
Location :
Surface: Growth limited to the agar surface.
Burrowing: Growing into the agar.
1.1.2. Cohesive growth : Continuous, thick, flat growth, nonspreading, with occasional discrete patches having no definite shape.

1.1.3. Colonial growth :
Type :
Filamentous:
Top view
Radial |
Trichomes generally diverging from the center. |

|
Skewed |
Trichomes generally growing in one direction. |

|
Irregular |
Trichomes growing randomly. |

|
Side view
Flat |
Planar growth along the agar surface. |

|
Penicillate |
Brush-like growth away from the agar. |

|
Burrowing |
Growth into the agar. |

|
Other types:
Top view
Round |
Circular. |

|
Elongated |
Colonies with unequal axes. |

|
Irregular |
Having no definable shape. |

|
Angular |
Colonies with relatively straight margins and corners. |

|
Side view
Flat |
Planar growth along the agar surface. |

|
Nippled |
Planar growth with a central protuberance. |

|
Low convex |
Section of a sphere with height smaller than 1/4 diameter. |

|
High convex |
Section of a sphere with height between 1/4 and 1/2 diameter. |

|
Globular |
Section of a sphere with height larger than1/2 diameter. |

|
Warty |
Having irregular protuberances resembling warts. |
|
Margin
Smooth |
Continuously even, without roughness. |

|
Rough |
Uneven margin without marked projections. |

|
Fingerlike |
Uneven margin with long projections. |

|
Aura-like |
Having a roundish diffuse growth zone spreading around a denser central zone. Frequently results from akinete migration and growth into filaments. |

|
1.2. Luster
Luster is observed by holding the plate between two fingers, placing it about 20 cm over a piece of white paper, and turning it forward and backward around a horizontal axis.
Dull : Lacking brilliance or luster. Usually observed with nonmucilaginous, mat-forming strains (i.e., Calothrix ) or strains forming filamentous colonies (i.e., Fischerella ).
Intermediate luster : Usually observed with mucilaginous strains of the spreading and aggregative types.
Glossy : Glistening, shiny. Usually observed with mucilaginous strains that form colonies.
1.3. Opacity
Opacity is observed by holding the plate between two fingers, placing it about 20 cm over a piece of white paper, and looking through it.
Opaque : Not permitting the passage of light.
Translucent : Permitting the passage of light.
Transparent : Can be seen through, e.g., mucilaginous colonies of some unicellular strains.
1.4. Color of the cyanobacterial material:
The color is defined by the combination of three descriptors:
Intensity: light, medium, or dark.
Modifier: greenish, yellowish, bluish, or reddish.
Base color: green or brown.
1.5. Color of the medium:
The color results from the diffusion of water-soluble pigments (e.g., phycocyanins, phycoerythrins) or other substances.
Four cases are distinguished: none, red/pink, yellow, and brown.
1. Criteria specific to solid cultures
2. Criteria specific to liquid cultures
3. Microscopic description
|